Osteoarthritis
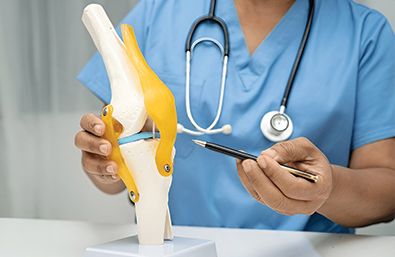
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis, affecting millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of bones gradually wears down, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. While osteoarthritis can affect any joint, it most commonly impacts the hands, knees, hips, and spine. Though the condition cannot be reversed, symptoms can be managed through lifestyle changes, medications, and medical treatments to slow its progression and improve joint function.
Symptoms of Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis symptoms typically develop slowly and worsen over time. Common signs include: Pain: Joints may hurt during or after movement.
- Stiffness: Joint stiffness is often most noticeable after waking up or following inactivity.
- Tenderness: Joints may feel tender when pressed.
- Loss of Flexibility: Range of motion may be reduced.
- Grating Sensation: Affected joints may make popping or crackling sounds.
- Bone Spurs: Extra bits of bone, felt as hard lumps, may form around joints.
- Swelling: Inflammation in soft tissues around the joint can cause swelling.
Causes of Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis occurs due to the gradual breakdown of cartilage, which is the smooth, protective tissue covering the ends of bones in joints. Over time, as cartilage wears away, bones begin to rub against each other, causing pain, stiffness, and inflammation. In addition to cartilage breakdown, osteoarthritis affects the entire joint, leading to bone changes, connective tissue deterioration, and inflammation of the joint lining.
Diagnosis of Osteoarthritis To diagnose osteoarthritis, a doctor will: Perform a Physical Exam: Checking for joint tenderness, swelling, redness, and range of motion. Order Imaging Tests: X-rays: Reveal cartilage loss by showing narrowed space between bones and bone spurs. MRI Scans: Provide detailed images of bones, cartilage, and soft tissues in complex cases. Conduct Lab Tests: Blood Tests: Rule out other forms of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Fluid Analysis: A small sample of fluid from the affected joint is tested to detect inflammation or infection. ** Managing Osteoarthritis**
Although osteoarthritis is a lifelong condition, individuals can manage symptoms by:
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce joint stress.
- Engaging in low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, and yoga.
- Using assistive devices (e.g., braces, walking aids) to reduce joint strain.
- Applying hot or cold therapy for pain relief.
- Practicing joint-friendly movements to avoid excessive stress.
Patient Stories
Overcoming Severe GI Bleeding: Mr. M. Ayyathurai's Inspiring Recovery at KIMSHEALTH, Nagercoil
Meet Mr. M. Ayyathurai, who successfully overcame severe GI bleeding with the de...
Dr. Jaipaul. Y
General Medicine