How Much Magnesium Glycinate Should I Take?
Magnesium is an essential mineral that supports muscles, bones, heart health, and the nervous system. Unfortunately, many people do not consume enough of it through diet alone. Conditions like diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), frequent alcohol use, or certain medications can also lower magnesium levels. At KIMSHEALTH Nagercoil, our specialists often meet patients who want to know if magnesium supplementation can help, and how much is safe to take.
What is Magnesium Glycinate?
There are several forms of magnesium supplements, but absorption rates vary. For example, magnesium oxide is cost-effective but not well absorbed, and is often used for constipation relief.
Magnesium glycinate (also called magnesium bisglycinate) is a form created by combining magnesium with glycine, an amino acid that supports relaxation. This type is highly bioavailable, meaning your body absorbs it efficiently through the small intestine. It is gentle on the stomach and generally well tolerated.
Benefits of Magnesium Glycinate
Research and clinical use have highlighted several magnesium glycinate benefits:
- Relieves anxiety and promotes relaxation
- Improves sleep quality (magnesium glycinate sleep support)
- Helps manage blood sugar in people with diabetes
- Supports bone strength and density
- Maintains normal heart rhythms
- Reduces premenstrual syndrome (PMS) discomfort
- May enhance exercise performance and reduce fatigue
- Shown in some studies to reduce migraine frequency
- Because it is well absorbed, magnesium glycinate is a preferred option for patients who need long-term supplementation.
Recommended Daily Intake
The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for magnesium depends on age and gender:
- Men (19–30 years): 400 mg
- Men (31 years and older): 420 mg
- Women (19–30 years): 310 mg
- Women (31 years and older): 320 mg
- Pregnant women: 350–360 mg
Since many supplements provide 100-200 mg per capsule, most adults may need one to two capsules daily, depending on dietary intake. The exact dosage should be confirmed by a doctor, particularly for patients with kidney conditions or those on long-term medications.
Signs of Magnesium Deficiency
About 60% of people may not meet their magnesium needs. Symptoms can include:
- Muscle cramps or twitches
- Fatigue and weakness
- Loss of appetite or nausea
- Tingling or abnormal heart rhythms in severe cases
At KIMSHEALTH Nagercoil, doctors may recommend a blood test if deficiency is suspected.
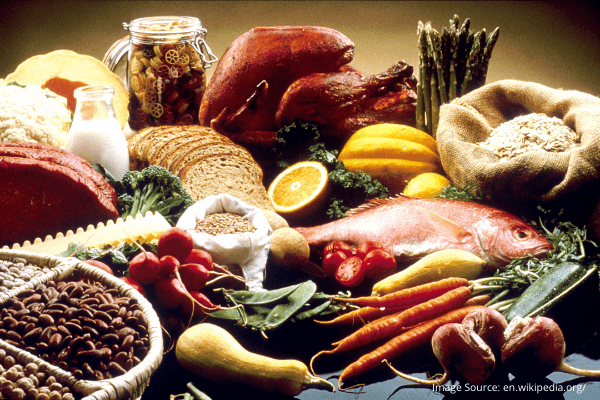
Natural Sources of Magnesium
Supplements are helpful, but including magnesium rich foods in your diet is equally important. Sources include:
- Leafy greens: spinach, kale, Swiss chard
- Nuts and seeds: pumpkin, chia, almonds, cashews
- Legumes: lentils, black beans, chickpeas
- Whole grains: oats, quinoa, brown rice
- Fruits: bananas, avocados, figs
- Fish: halibut and mackerel
- Dark chocolate (in moderation)
- Eating a balanced diet along with supplementation ensures healthy magnesium levels.
Risks of Excess Magnesium
For most healthy people, the kidneys regulate excess magnesium. However, very high intake from supplements may cause:
- Low blood pressure
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea or stomach upset
- Irregular heartbeat
- Muscle weakness
This is why dosage should be adjusted under medical supervision.
Guidance from KIMSHEALTH Nagercoil
If you are considering magnesium glycinate for better sleep, stress management, or overall health, speak with a healthcare professional first. Our Internal Medicine department at KIMSHEALTH Nagercoil guide patients on safe supplementation, diet planning, and monitoring possible interactions with medications.
The right intake of magnesium can support your energy, heart, and sleep, but the safest approach is to let medical experts help you decide how much is suitable for your needs.
Ten Effective Remedies That You Can Refer to When You Are Suffering from Muscle Cramps
Finally starting off with the gym life can get too overwhelming until you hit those muscle cramps along with the weights.
ICSI(Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection)
Normally during every mid-menstrual period, one of the 2 ovaries releases an ovum. Each ovum is covered by a membrane called follicle,
Pregnancy and Delivery Care
Nothing could possibly compare to the joy of becoming a parent. After nine long months of waiting, the moment you have been waiting for is almost there:
Some Common Causes of Chest Pain
The first thing that jumps into the mind whenever you have some sort of chest pain is heart attack! It’s only human to feel that way
Organic Food Vs GMO Food: What Should You Pick?
There is no doubt that the quality of food we consume is crucial for our good health. And with more people becoming health conscious the d
Importance of Breastfeeding and Vaccinations for Newborns
Going nature’s way is best when it comes to providing nourishment for the apple of your eye – your baby. Breast milk is best for your baby as it
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL): A Breakthrough in Kidney Stone Treatment
Kidney stones, those small, hard mineral deposits that form in the kidneys, can cause excruciating pain and discomfort.
Skin Tags - Benign Tumor or Cancerous Tumor?
Skin tag if observed is a narrow stalk that hangs about your skin, bulging at the end. They are usually freshly colored and can grow anywhere on your body.
3 Ways Vitamin C is Helpful for the Immune System
The water-soluble vitamin, Vitamin C is also known as ascorbic acid. It is helpful in building up the blood vessels, skins, and making bones stronger
4 Signs of Mental Illness
As life has gotten fast and hectic, different health issues have got introduced lately. Not just physical issues,
4 Ways Night-Shifts Can Be Dangerous For Your Menstruation And Ovulation
A good night's sleep is of value for pregnant women. But with strenuous work-hours and shift work, sleep can quite a luxury for all.
Causes Of Infertility in Women
More and more women are putting off pregnancy till well into their 30’s or early 40’s for career reasons; infertility is fast becoming a major heartbreaking issue for such couples.
Do Not Indulge in These 9 Common Dieting Mistakes
Dieting is not just about eating less or starving yourself to meet unrealistic goals. Healthy dieting involves making informed food choices.
Laryngeal Reiinervation Procedure at KIMS Hospital
Mr. K.P 56-year-old business executive from Bangalore underwent a thyroid surgery two years back.
Learn How Stress Affects Your Heart Health
Stress is a frequent side effect of the modern 21st Century lifestyle. We’re always running around to meet deadlines, pay bills we tend to
Lose Weight: The Healthy Way
Almost everyone we know is worried about the way they look. There are several concerns people have, like their complexion
Myths About Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric surgery – be it the gastric bypass and other weight-loss surgeries – involve making changes to your digestive system to help you lose weight.
Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Should You be Worried?
A recent study has found that 1 in 5 people in India suffers from liver disorders. Before you blame it on the increased alcohol consumption
Obesity and its Relation to Type 2 Diabetes
Diabetes is a condition that arises when the body doesn’t produce enough insulin,, hence there is excess glucose in the blood
Rotator Cuff Tear
A rotator cuff tear is a rotator cuff injury that can cause shoulder pain and loss of arm function. The rotator cuff is a set of muscles and tendons in your shoulder.
What Happens to Your Body When You Fast?
Fasting has been practised by humans for thousands of years as a way of rejuvenating the mind, body and soul and as a common ritual of many religions from all over the world
Why You Shouldn’t Consume Medicines with Cold Water
There has been a long-raging debate on the temperature of water needed for consuming medications. You won’t find much as in research papers
10 Tasty Delicious Diabetic-Friendly Recipes
Worry about it no more, as a healthy diabetic diet does not have to be bland. Instead, you can enjoy a myriad of flavorful, low-calorie
4 Not So Common Health Problems in Teenagers
The current generation of teenagers have far more access to technology and gadgets than their parents did.
4 Secrets to Adjusting Your Toddler's Sleep Cycle
Most of the parents, some time or the other, may have faced the trouble of making their toddlers sleep at night.
Related Blogs
Ten Effective Remedies That You Can Refer to When You Are Suffering from Muscle Cramps
Finally starting off with the gym life can get too overwhelming until you hit those muscle cramps along with the weights.
ICSI(Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection)
Normally during every mid-menstrual period, one of the 2 ovaries releases an ovum. Each ovum is covered by a membrane called follicle,