

CAUSES OF INCREASED INFERTILITY IN MEN
Infertility in men has been increasing at an alarming rate over the past few years; incidences have increased by at least three-fold over the past five years. Doctors proclaim that about 30% of the infertility cases seen currently in India are due to problems with the man. They are of the opinion that factors like stress, environmental pollution, chemical toxins and altered lifestyles are to blame for ruining the quality of semen and dropping sperm counts.
Male infertility refers to the inability of a male to cause pregnancy in a healthy, fertile female. It is found that one in every twenty men has some sort of fertility issue associated with low sperm counts in the ejaculate. While more than 90% of male infertility cases are due to low sperm counts or poor quality of sperms, or both, the remaining percentage is due to a wide and varied range of conditions. These can include anatomical factors like undescended testicles, hormonal imbalances, environmental factors, infections, diabetes, stress, genetic defects, etc.
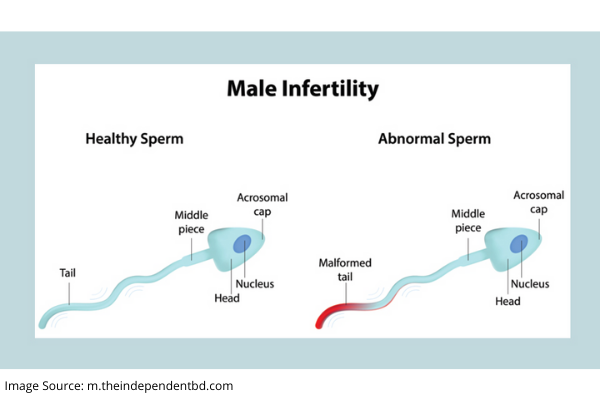
Sperms are the male eggs and any defect or abnormality in their structure becomes critical to inducing pregnancy. In about 15% of male infertility cases, there are no viable sperms present in the semen, a condition known as azoospermia. Some of the other causes of male infertility include the following:
Variocele – This is due to improper circulation of blood within the testicles, leading to its getting engorged and increasing in temperature, which hinders sperm production.
Undescended testicles – Ideally, the testicles are supposed to descend into the scrotum shortly after birth, and when this doesn’t happen, a condition known as cryptorchidism arises. Decreased fertility is more likely in such men.
Tumors – Malignant testicular cancer sometimes develops in the testicles, destroying its ability to produce sperms. Tumors arising in hormone producing glands such as the pituitary gland can also affect the male reproductive organ negatively.
Physical defects – In a small number of people, there may be a blockage or malformation defect in the urethra that prevents sperms from combining with the semen fluid. The blockage can also be due to injury from surgery, trauma or prior infections.
Mumps – Contracting this viral infection after puberty can damage the tissues involved in producing sperms – in some cases the damage is permanent. Infections like gonorrhea, Chlamydia and HIV can also lead to testicular damage.
Hormone imbalance – Abnormalities in the hormonal glands such as the pituitary, thyroid, hypothalamus or adrenal glands can lead to low testosterone levels
Environmental causes – Over-exposure to industrial chemicals, heavy metals, radiations, x-rays or overheating of the testicles are some of the work-related hazards that can lead to reduced sperm production or abnormal, defective sperms.
Lifestyles – Indulging in illicit drugs, alcohol overuse, smoking or emotional stress and obesity can all lead to reduced male fertility.
Being informed about these possibilities should empower men to be more vigilant about their fertility….














