

POLYCYSTIC OVARY DISEASE
Polycystic Ovary Disease – What is it?
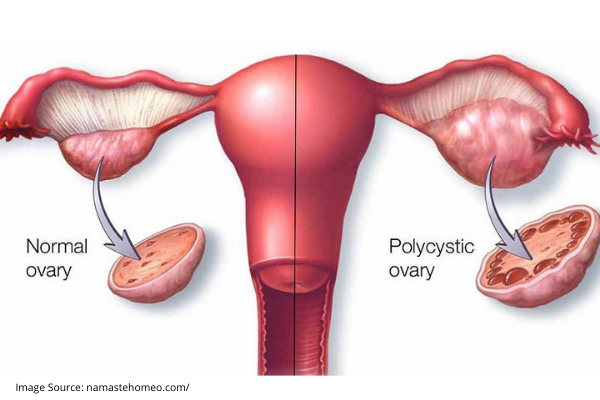
During every menstrual cycle, follicles develop in the ovaries. Out of these only follicle matures. This mature follicle ruptures and enters the fallopian tube. This is ovulation. Remaining follicles get destroyed.
In a few women, ovaries are larger than normal with immature follicles stuck to each other like pearls in a necklace. This is Polycystic Ovary. Usually, this is not dangerous or a reason for infertility. But associated hormonal imbalance leads to clinical features called polycystic ovary and polycystic ovary syndrome. Everyone with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome will have Polycystic Ovary but not vice versa.
What are the symptoms?
All the symptoms need not appear in all patients. 1 or more of the following symptoms can appear in a patient with Polycystic ovary syndrome in additions to Polycystic Ovaries.
- Excessive facial and body hair growth (Hirsutism)
- Irregular or absent periods
- Infertility
- Obesity
- Repeated abortions
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome – Threat to health!
Neglecting PCOC- leads to long-term health problems
- Diabetes
- Pregnancy-related complications
- Cancer
- Disease-related complication
- Diseases related to Heart and blood vessels
- 40% of patients with polycystic ovary syndrome around the age of 10 years – are at risk of developing abnormal blood sugar levels and diabetes in future.
- Other than infertility, PCOS can cause Repeated abortionIncrease risk of Diabetes and hypotension during the pregnancy and retarded growth of babies in such mothers.
- Increased risk of endometrial cancer (cancer of the uterus)
Treatment/ Solution
- Weight loss- by exercise and dieting.
- Healthy living
- For Irregular Periods – Oral hormonal medication
- For Infertility- Weight boss and laparoscopy if required.
- For Pregnancy in a patient with PCOS
- Close monitoring of blood sugar
- Early detection and control of diabetes














