

SIGNS OF TESTICULAR CANCER
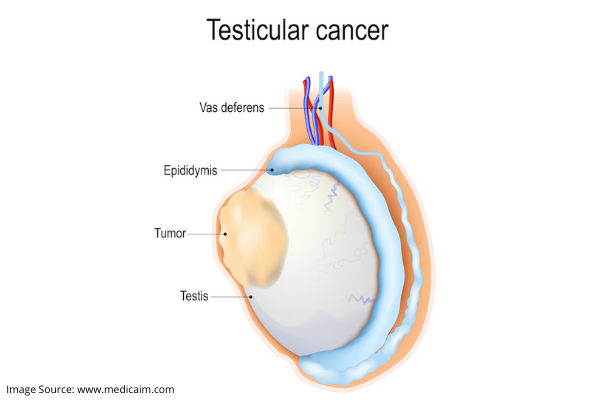
Men have a pair of testicles located in a sac-like pouch called the scrotum. It forms part of their reproductive system and are responsible for sperm production. Cancer of the testicles can be potentially deadly – just like most other cancers. It accounts for about 1.2% of all male cancers and is responsible for 11-13% of all cancers in men between the ages of 15-35 years age. However, about 90-95% cases of testicular cancers are curable, even if do they become metastatic.
Testicular cancer basically presents as an enlarged testicle or small, hard lumps growing on it. Other symptoms usually do not occur until the cancer has spread elsewhere. Here are some common signs and symptoms of testicular cancer:
A usually painless pea-sized lump on a testicle is the first sign.
The testicle or scrotum could become enlarged.
The testicle could start to shrink.
There could be a fluid collection in the scrotum.
Feeling of heaviness in the scrotum.
Pain in the testicle.
Dull ache in the lower abdomen or groin.
Lower back pain.
Enlargement of breasts (gynecomastia).
Swollen lymph nodes around the region.
Swelling in one or both leg.
Early detection is the best form of protection. You could try spending just 3 minutes self-examining yourself once a month; the best time would be after a warm bath when the scrotal skin is soft and relaxed. Try to gently roll the testicles between the thumbs and fingers and check for any hard lumps. While all lumps aren’t necessarily malignant, do check in with a doctor.
There can be some overlap in signs and symptoms of testicular cancer and some other disease conditions. Hence only a qualified doctor can make a diagnosis after a series of tests, history taking and physical examination. Sometimes conditions like hydrocele (build-up of fluid around the testicles), varicocele (enlargement of a blood vessel near the testicle), hernia (opening in the abdominal muscle), cysts or localized infections can all produce similar signs and symptoms overlapping that of testicular cancer. Sometimes twisting of vessels within the scrotum or some injury can also lead to similar signs.
Testicular cancer develops when cells within the testicles change in character and start to multiply out of control, forming a mass called a tumour. A malignant tumour is almost always curable when detected early on, but is curable at later stages too. Signs and symptoms of advanced testicular cancer include fatigue, weight loss, shortness of breath, chest pain, headaches, confusion, stomach pain and low back pain. In some case, there is DVT (deep venous thrombosis), bloody sputum or pulmonary embolism.














