

TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR SCOLIOSIS
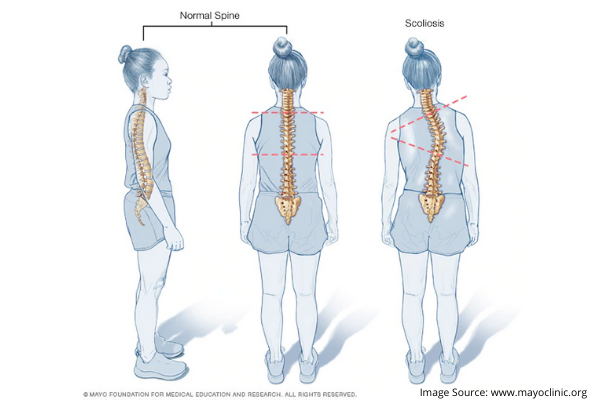
Scoliosis is an abnormal condition of the spine where there is a sideways curve to the backbone or spine. Upon X-ray, it presents as S- or C-shaped spine. This is a chronic condition that may last a lifetime and doesn’t really need a diagnostic procedure as its self-diagnosable.
In India, more than 10 million cases of scoliosis occur every year and the condition can affect any age group, but is usually more common in those between the ages of 10-12 during the growth spurt just before puberty with higher incidences in girls than boys. The condition is usually mild in most people with only a few symptoms occurring in majority of the cases. Some people develop scoliosis that gets worse with time, leading to a painful and disabling life.
Usually no treatment is required in majority of the cases, although periodic check-ups are recommended to keep tabs on the angle of deformity. When planning a treatment regime for the person with scoliosis, knowing if the curve is likely to worsen is crucial to the treatment plan; other factors include the physical condition and age of the person and how much more she/he is likely to grow physically as well as the type of scoliosis.
Other factors include the fact that S-shaped curves tend to worsen more often than C-shaped curves, with larger curves more likely to worsen over time. If the curve is located at the central thoracic region of the spine, there are greater chances of its worsening than if it’s located above or below this area.
A brace is usually brought into the picture when the side-to-side curve in the spine progresses by at least 5 degrees in a 4-6 month period or if the angle goes beyond 25-30 degrees with still a significant amount of skeletal growth still remaining for the afflicted person. Bracing is the first line of treatment and is a big time commitment for it to be effective. It can either be worn only at bedtime or continuously and though it is uncomfortable, both physically as well as emotionally, it does succeed in controlling further worsening of the curvature and associated symptoms.
As the condition worsens, it can lead to pressure on the spinal cord resulting in loss of coordination of the leg muscles along with an associated abnormal gait; it can also lead to deformity of the chest in severe cases, resulting in breathing problems, fatigue and even heart failure.
In such severe cases, surgery becomes the next option. The purpose of the surgery is to stop the worsening of the curve progressing, correct the deformity as well as provide trunk balance maintenance. There are three types of surgeries used for scoliosis:
- Fusion surgery where two adjacent vertebras are permanently fused to become immobile.
- Growing systems where rods are placed adjacent to the spine to keep the spine growing straight.
- Fusion-less surgery is a new approach used to create balance by using growth modulation on the spine.














