

UNDERSTANDING NERVES AND NEURONS
Did you know that there are approximately 86 billion neurons in your brain! And what do they do? They’re the reason why your brain transmits information to other organs of the body. They’re connected with other neurons to allow the brain to think, act, and perform all activities. Here’s a simple guide to help you understand nerves and neurons:
What is a Neuron?
They’re cells within the nervous system; a neuron is the most basic building block of the brain. While they may seem similar to other cells in the body, there’s one primary difference- neurons transmit information within the body. This is done through chemical and electrical impulses. And unlike other body cells, they do not reproduce after birth, but create new connections. There are more than 10,000 different types of neurons, but by a general classification, you can divide them into three categories, sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons.
Sensory Neurons:
Sensory neurons communicate with the central nervous system by responding to touch, sight, hearing, taste, smell, etc. They send information from the skin, eyes, ears, nose, and tongue.
Motor Neurons:
Motor neurons are responsible for involuntary muscle functions like the beating of the heart, passage of food, breathing, etc.
Interneurons:
Interneurons are found in the central nervous system and connect the sensory and motoneurons. They send information between these neurons.
Parts of a Neuron:
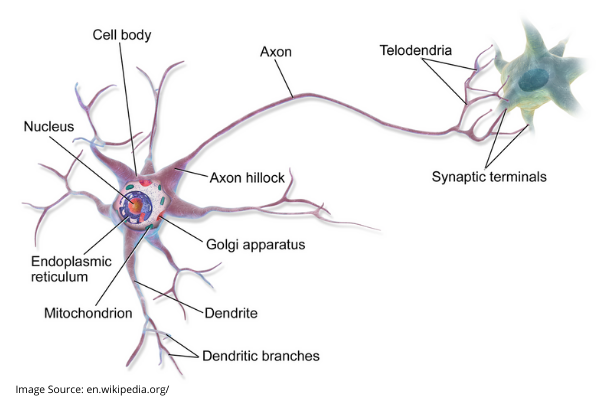
A neuron is made up three parts, viz. the cell body or soma, dendrites (aka signal receivers), and an axon. The cell body has a nucleus with at least one nucleolus and many cytoplasmic organelles. Dendrites are extensions that send and receive signals from other neurons. While some cells have few dendrites, other cells have highly branched dendrites to help them receive information. Axons also take information from other cells in the body. When in a bundle, they are called nerves. The longest axon in the body runs for around 3 feet- from the bottom of the spine to the toe.
Synapses, Neurotransmitters, and more:
Cells when connecting with one another are called synapses. As mentioned earlier, neurons communicate using electrical impulses and chemical messengers. Once an electrical impulse reaches the end of the axon, a message is transmitted to the dendrite of an adjoining neuron. Sometimes this impulse is instantly transmitted, and sometimes, this is done through neurotransmitters. Scientists have identified around 100 such neurotransmitters, including endorphins, dopamine, and acetylcholine.
Common Neurological Disorders:
Although there are more than 600 neurological ailments, the most common among them are:
Alzheimer’s Disease/Dementia and Disorders Affecting Memory Functions:
These are neurodegenerative diseases that affect a person’s memory and causes problems with thinking and behavior.
Migraines:
A migraine refers to an intense headache that can cause nausea, sensitivity to light, sound, or smell, etc. While scientists do not know what could trigger a migraine, some of the causes could include irregularities in the brain’s blood vessels.
Parkinson’s:
Parkinson’s is a motor system disorder resulting from the loss of dopamine-producing neurons.
Keeping Your Brains Healthy:
With a little effort, you can keep your mind fit and active. Learn a new language. Take up a new hobby. Eat a healthy diet. Keep a Rubik’s cube. Stay connected with family and friends.














